AI plays a crucial role in the global cultural ecosystem. It recommends what we should see, listen to, read, and buy. It determines how many people will see our shared content. It helps us make aesthetic decisions when we create media. In professional cultural production, AI has already been adapted to produce movie trailers, music albums, fashion items, product and web designs, architecture, etc. In this short book, Lev Manovich offers a systematic framework to help us think about cultural uses of AI today and in the future. He challenges existing ideas and gives us new concepts for understanding media, design, and aesthetics in the AI era.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

Dr. Lev Manovich is the author and editor of 13 books including Theories of Software Culture, Instagram and Contemporary Image, Software Takes Command, and The Language of New Media which was described as “the most suggestive and broad ranging media history since Marshall McLuhan.” He was included in the list of “25 People Shaping the Future of Design” in 2013 and the list of “50 Most Interesting People Building the Future” in 2014. Manovich is a Professor of Computer Science at The Graduate Center, CUNY, and a Director of the Cultural Analytics Lab that pioneered analysis of visual culture using computational methods.
https://strelka.com/en/press/books/lev-manovich-ai-aesthetics
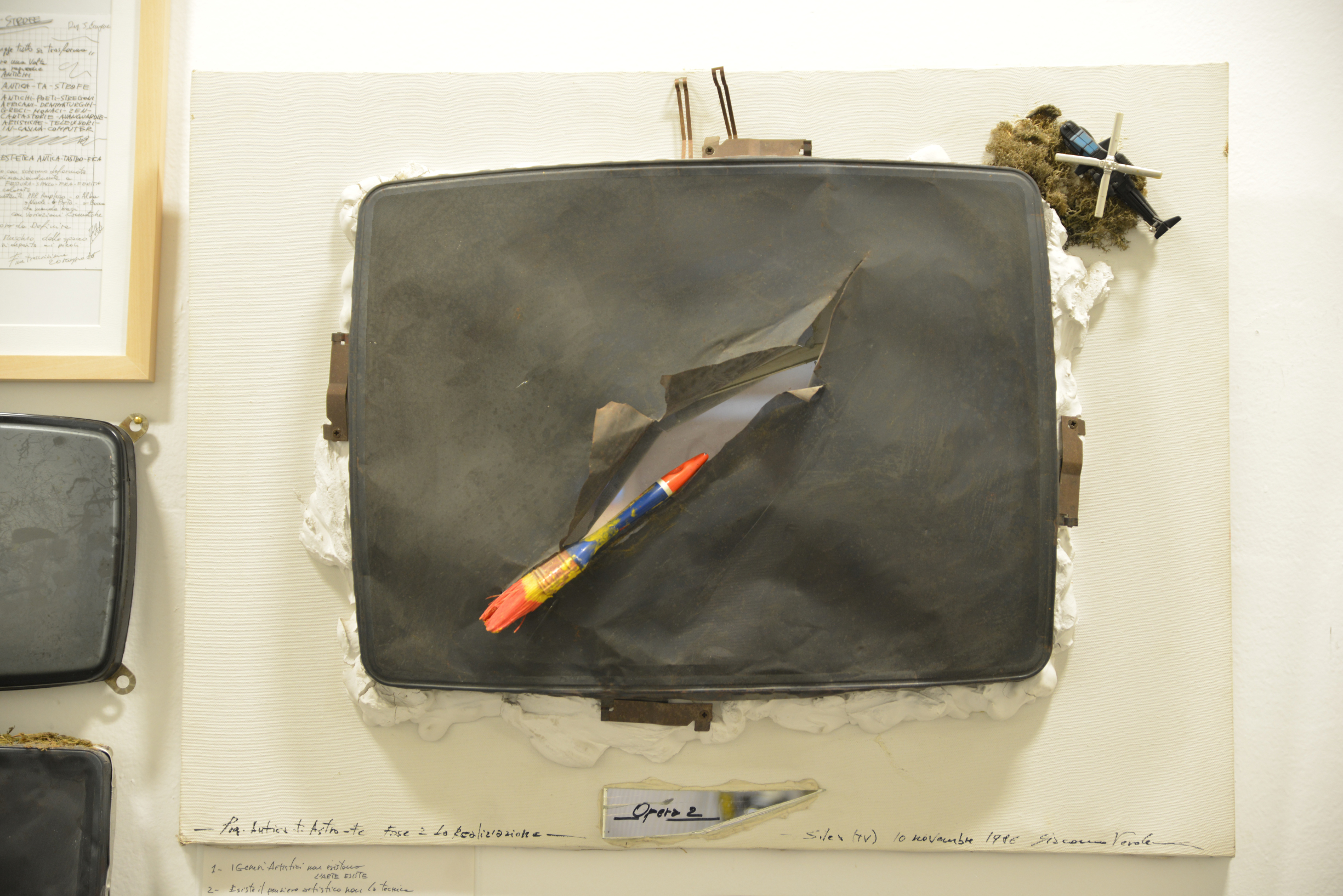
Un estratto di “AI Aesthetics” dal sito di STRELKA PRESS
LEV MANOVICH
In the original vision of AI in the 1950s-60s, the goal was to teach a computer to perform a range of cognitive tasks. According to this projection, a computer would simulate many operations of a single human mind. They included playing chess, solving mathematical problems, understanding written and spoken language, and recognizing the content of images. Sixty years later, AI has become a key instrument of modern economies, deployed to make them more efficient, secure, and predictable by automatically analyzing medical images, making decisions on consumer loans, filtering job applications, detecting fraud, and so on. AI is also seen as an enhancer of our everyday lives, saving us time and effort. A good example of this is the use of voice interface instead of typing.
But what exactly is “Artificial Intelligence” today? Besides original tasks that defined AI such as playing chess, recognizing objects in a photo, or translating between languages, computers today perform endless “intelligent” operations. For example, your smartphone’s keyboard gradually adapts to your typing style. Your phone may also monitor your usage of apps and adjust their work in the background to save battery. Your map app automatically calculates the fastest route, taking into account traffic conditions. There are thousands of intelligent, but not very glamorous, operations at work in phones, computers, web servers, and other parts of the IT universe.
Therefore, in one sense, AI is now everywhere. While some AI roles attract our attention – such as Google’s Smart Reply function that suggests automated email replies (used for 10% of all answers in Google’s Inbox app in 2017) – many others operate in the gray everyday of digital society.
[…]
Will AI replace professional cultural creators – media, industrial, and fashion designers, photographers and cinematographers, architects, urban planners, and so on? Will countries and cities worldwide compete as to who can more quickly and better automate their creative industries? Will countries and cities (or separate companies) that figure out how best to combine AI and human skills and talents get ahead of the others?
Today AI gives us the option to automate our aesthetic choices (via recommendation engines), assists in certain areas of aesthetic production such as consumer photography, and automates other cultural experiences (for example, automatically selecting ads we see online). But in the future, it will play a larger part in professional cultural production. Its use of helping to design fashion items, logos, music, TV commercials, and works in other areas of culture is already growing. But currently, human experts usually make the final decisions or do actual production based on ideas and media generated by AI.
The well-known example of Game of Thrones is a case in point. The computer suggested plot ideas, but the actual writing and the show’s development was done by humans. We can only talk about fully AI-driven culture where AI will be allowed to create the finished design and media from beginning to end. In this future, humans will not be deciding if these products should be shown to audiences; they will just trust that AI systems know best – the way AI is already fully entrusted to choose when and where to show particular ads, as well as who should see them.
We are not there yet. For example, in 2016 IBM Watson created the first “AI-made movie trailer” for the feature film Morgan (Mix, 2016). However, AI only chose various shots from the completed movie that it “thought” were suitable to include in the trailer, and a human editor did the final selection and editing. In another example, to create a system that would automatically suggest suitable answers to the emails users receive, Google workers first created a dataset of all such answers manually. AI chooses what answers to suggest in each possible case, but it does not generate them. (The head of Google’s AI in New York explained that even one bad mistake in such a scenario could generate bad press for the company, so Google could not risk having AI come up with suggested answer sentences and phrases on its own.)
It is logical to think that any area of cultural production which either follows explicit rules or has systematic patterns can be in principle automated. Thus, many commercial cultural areas such as TV dramas, romance novels, professional photography, music video, news stories, website and graphic design, and residential architecture are suitable for automation. For example, we can teach computers to write TV drama scripts, do food photography, or compose news stories in many genres (so far, AI systems are only used to automatically compose sports and business stories). So rather than asking if any such area will be automated one day or not, we need to assume that it will happen and only ask “when.”
This sounds logical, but the reality is not so simple. Starting in the 1960s, artists, composers, and architects used algorithms to generate images, animations, music, and 3D designs animations, music, and 3D designs (“Computer Art,” n.d.). Some of these works have entered the cultural canons. They display wonderful aesthetic inventiveness and refinement. However, in most cases they are abstract compositions with interesting and complex patterns, but without direct references to the human world. Think of such classics as abstract geometric images by Manfred Mohr (1969-1973) (Mohr, n.d.), John Whitney’s computer animation Arabesque (1975), or Iannis Xenakis’s musical compositions Atres and Morsima-Amorsima (1962) (Maurer, 1999). There is no figuration in these algorithmically-generated works, no characters like in novels, and no shots of the real world edited together into narratives like in feature films.
Now compare these abstract algorithmic classics with current attempts to automatically synthesize works that are about human beings, their worlds, their interests, emotions and meanings. For example, today Google Photos and Facebook offer users automatically created slideshows and videos edited from their photos. The results are sometimes entertaining, and sometimes useful, but they can’t be yet compared to professionally-created media. The same applies to images generated by Google engineers using DeepDream neural net (2015-) and later by others who used the same technology (DeepDream, n.d.). These AI creations in my view are more successful than the automatically-generated slideshows of user photos, but this is not because DeepDream is a better AI. The reason is that 20th century visual art styles tolerate more randomness and less precision than, for example, a photo narrative about a trip that has distinct conventions and restrictions on what and can be included and when. Thus, in the case of DeepDream, AI can create artistically plausible images which do refer to the human world because we consider it “modern art” and expect big variability. But in the case of automatically edited slideshows, we immediately know that the computer does not really understand what it is selecting and editing together.
You can buy the e-book version here.
AI